Table of Contents
ToggleImagine walking into a hospital where doctors don’t just rely on textbooks and charts but also have a digital assistant that overlays vital information right before their eyes. Welcome to the world of augmented reality (AR) in healthcare, where the future isn’t just bright—it’s downright dazzling.
AR is revolutionizing how medical professionals diagnose, treat, and educate. From training surgeons with lifelike simulations to helping patients visualize their treatment plans, this technology is like having a superhero sidekick in scrubs. It’s not just about fancy gadgets; it’s about improving outcomes and making healthcare more accessible. As AR continues to evolve, it’s time to explore how it’s transforming the medical landscape and why it’s not just a trend, but a game changer in the fight for better health.
Overview of AR for Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) transforms healthcare by providing innovative solutions for various medical applications. Medical professionals utilize AR to visualize complex data in real-time, enhancing decision-making during procedures. Surgeons benefit from AR by overlaying digital images onto a patient’s anatomy, enabling precise navigation and improved outcomes.
Education in healthcare also sees significant advancements through AR. Medical students and residents engage with 3D models that simulate human anatomy, fostering a deeper understanding of complex biological systems. This immersive learning experience enhances retention and application of knowledge in real situations.
Patient engagement improves with AR, as individuals gain access to interactive representations of their health conditions. Understanding treatment plans becomes easier when patients visualize anatomical structures, thereby increasing compliance and satisfaction. For example, a patient might use AR to explore a virtual model of their surgery, which demystifies the procedure.
Integrating AR technology into diagnostics leads to better accuracy and faster results. Techniques like augmented imaging assist radiologists by highlighting critical regions on scans, streamlining the diagnostic process. These capabilities emphasize AR’s role in reducing errors and enhancing patient safety.
Various healthcare sectors, including surgery, rehabilitation, and mental health, have begun embracing AR applications. Rehabilitation specialists employ AR to create engaging exercises that motivate patients through gamification, promoting regular activity and adherence to recovery plans. Mental health practitioners use AR for exposure therapy, allowing individuals to confront fears in a controlled environment.
As AR continues to advance, it becomes more accessible and affordable. Manufacturing costs decrease, and devices become more user-friendly, supporting widespread adoption. The future of AR in healthcare looks promising, with potential for continuous evolution in patient care and medical education.
Benefits of AR in Healthcare
AR technology offers numerous advantages in the healthcare sector. Significant improvements include surgical precision and enhanced patient involvement.
Enhanced Surgical Accuracy
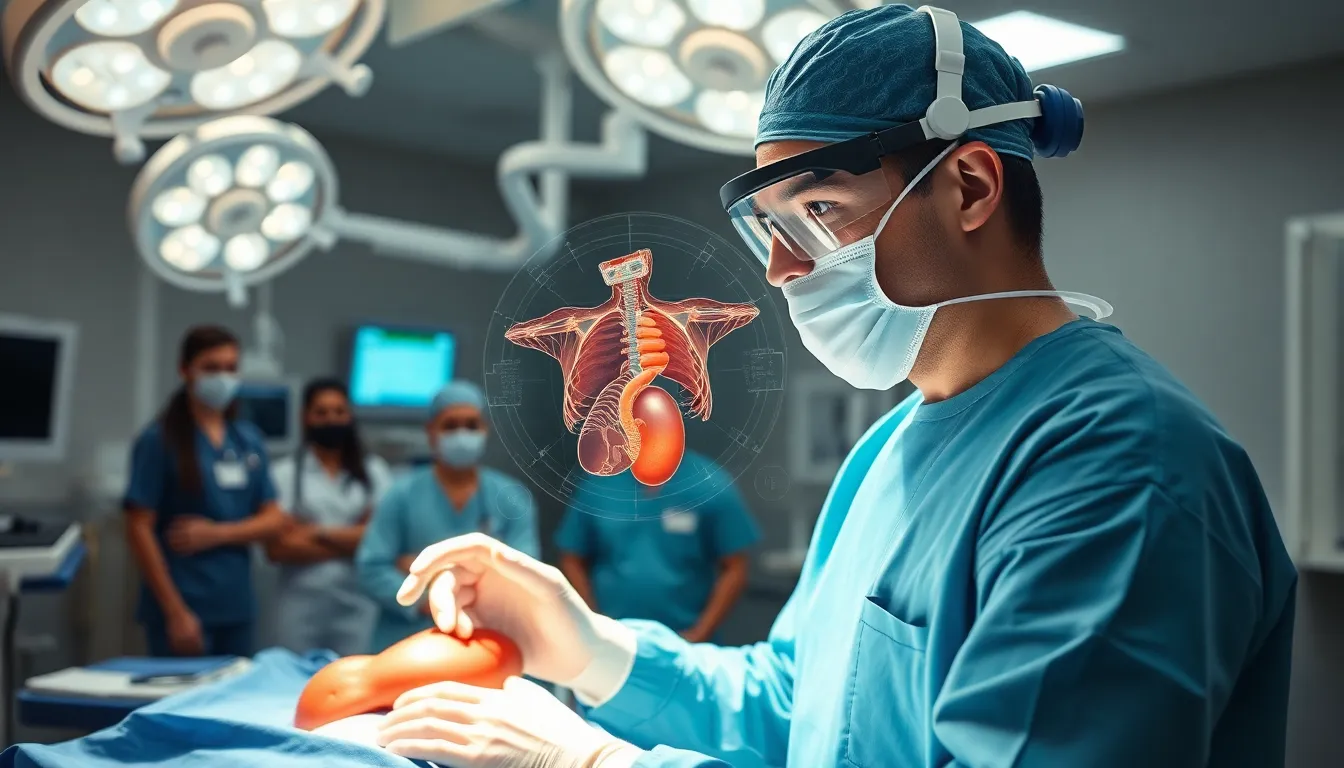
Surgeons benefit from AR’s capability to overlay critical patient data directly into their field of vision. This allows them to visualize anatomy in real-time during procedures. Research indicates AR can increase surgical accuracy by up to 30%. Surgeons experience better depth perception when manipulating instruments, as AR aids in complex procedures. Training simulations create realistic environments for surgeons, fostering skill development before actual surgeries. The incorporation of AR in surgical theaters promotes collaboration among medical teams, ensuring that each professional operates with a complete understanding of the procedure.
Improved Patient Engagement
Patients gain a clearer understanding of their health with AR’s interactive visuals. This technology helps them visualize their conditions and treatment processes, resulting in increased comprehension and reassurance. Studies show that patients who access AR features report higher levels of satisfaction. Additionally, AR can personalize treatment plans by tailoring visuals to specific patient needs. Enhancing the patient experience often leads to better adherence to prescribed therapies. AR applications in health education foster informed discussions between patients and healthcare providers, reinforcing trust and compliance in treatment.
Challenges in Implementing AR Technology
Implementing AR in healthcare presents several challenges that need addressing for successful integration.
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations pose significant obstacles to AR adoption. Compatibility issues with existing medical equipment can hinder seamless integration. Insufficient processing power in some devices restricts the complexity of AR applications. Additionally, creating high-quality 3D models requires advanced imaging techniques, which may not be universally available. AR applications often demand robust connectivity, and inadequate network infrastructure can disrupt their functionality. Furthermore, the need for ongoing updates and maintenance can burden healthcare IT departments, consuming valuable resources.
Cost Constraints
Cost constraints significantly impact the widespread adoption of AR. High initial investment costs for AR hardware and software can deter healthcare organizations from making the leap. Developing custom AR solutions tailored to specific medical needs incurs substantial development expenses. Training staff to effectively utilize AR technology requires both time and additional financial resources. Budget limitations in healthcare often prioritize essential services over technological advancements. Balancing these costs against potential benefits presents a challenge, particularly for smaller facilities with limited operating budgets.
Real-World Applications of AR for Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) has numerous applications in healthcare, enhancing training, diagnosis, and treatment.
Medical Training and Education
Medical students engage with AR to gain immersive experiences. Through three-dimensional models, they explore human anatomy in a realistic way. Such interactive functionality fosters better retention and understanding of complex concepts. Training programs increasingly integrate AR, allowing learners to visualize and manipulate anatomical structures. By simulating real-world scenarios, students practice procedures in a risk-free environment. This hands-on approach improves skills and builds confidence before entering clinical settings. As a result, institutions report higher competency levels among graduates using AR technologies.
Patient Diagnosis and Treatment
AR plays a crucial role in patient diagnosis and treatment planning. Radiologists rely on augmented imaging to pinpoint critical areas within scans accurately. It enhances diagnostic precision by overlaying important data directly onto images. Surgeons utilize AR to visualize patient-specific information during procedures, reducing the risk of errors. This technology aids in explaining health conditions effectively to patients, leading to improved adherence to treatment plans. Interactive visuals help patients understand their diagnoses and proposed therapies effortlessly. Overall, AR transforms how healthcare professionals deliver tailored patient care.
Future Prospects of AR in Healthcare
Innovative advancements in augmented reality promise to reshape healthcare’s future significantly. Expect an increase in AR applications that enhance both surgical and diagnostic processes. Surgeons will likely rely on AR for dynamic overlays that improve precision and inform decision-making in real time.
Education will also see significant changes, with medical students obtaining more experiential learning opportunities through immersive AR simulations. This trend encourages greater retention of complex concepts, resulting in better preparedness for clinical environments.
Patient engagement is set to improve rapidly, as AR provides visuals that clarify treatment plans. Enhanced understanding fosters compliance, ensuring patients follow their healthcare directives diligently.
AR technology is projected to expand in rehabilitation, using gamified experiences to boost motivation among patients. Rehabilitation specialists can customize these experiences based on individual patient needs, leading to more effective recovery pathways.
Mental health practitioners are exploring AR’s potential for exposure therapy, showing promising results in managing anxiety and phobias. Tailored experiences allow patients to confront concerns in controlled settings, enhancing therapy effectiveness.
As affordability rises, healthcare organizations will increasingly adopt AR solutions. Reducing costs associated with implementation will likely encourage smaller facilities to invest in this transformative technology.
Collaboration between healthcare teams will also escalate, with AR facilitating real-time sharing of patient information during procedures. Enhanced communication fosters better teamwork, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Opportunities for continued research and development in AR applications can lead to groundbreaking innovations that further integrate technology into everyday healthcare practices.
The integration of AR in healthcare is reshaping the landscape of medical practice and education. As this technology evolves it promises to enhance surgical precision and improve patient understanding of their health. With immersive training experiences for medical students and real-time data visualization for professionals AR is set to revolutionize how care is delivered.
Despite challenges in implementation the potential benefits far outweigh the obstacles. As costs decrease and accessibility improves more healthcare organizations will likely embrace AR solutions. This shift could lead to better collaboration among healthcare teams and ultimately result in improved patient outcomes. The future of AR in healthcare is bright and full of possibilities that could transform the way medical professionals operate and engage with patients.